Some states conduct more extensive background checks that include investigating known associates and denying licenses for any felony convictions. Texas makes opening a restaurant a possibility for a wider range of people who have some black marks in their past.
Houston’s culinary scene has never been more dynamic, and there’s plenty of room to expand in a city and state known for wide-open spaces. Starting a restaurant, bar or food truck business in Houston is easy with an organized plan. According to an article posted in Food & Wine online magazine, the city welcomes the kind of experimental entrepreneurs who can’t afford to open restaurants in most major urban centers. David Chang recently suggested that Houston was the most exciting city in the United States for food culture. Anthony Bourdain became a fan after discovering that the city’s culinary options went far beyond exceptional barbecue.
Opening a restaurant in Houston is a fairly straightforward process, and there are few of the bureaucratic barriers that are common for food entrepreneurs when opening a restaurant in San Diego or trying to get a food truck a meaty role in Los Angeles’s food culture.
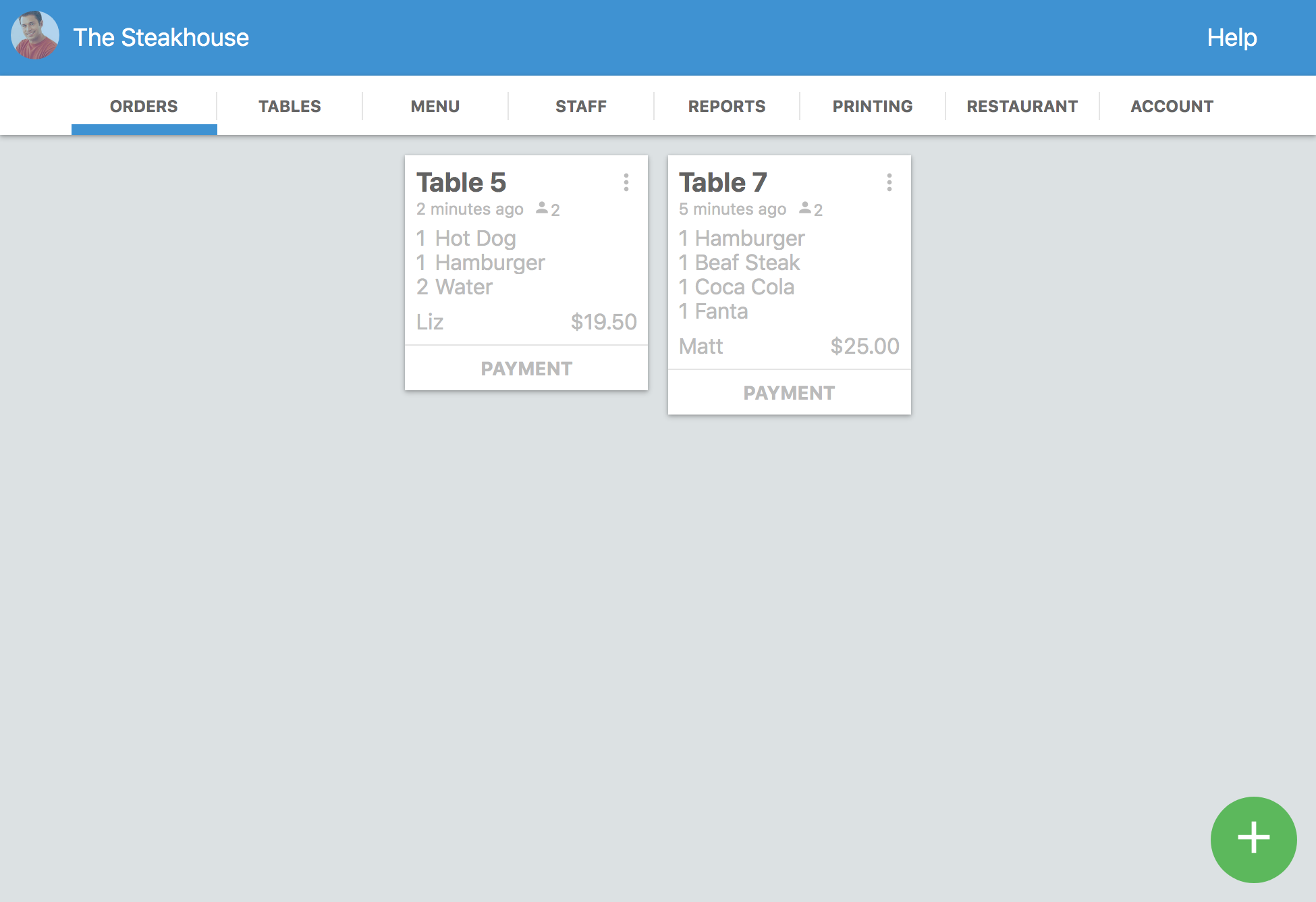
Starting a restaurant business in Houston requires getting your business license, registering with the city, state and federal authorities, picking a business structure, choosing and registering a fictitious business name, getting a health permit and getting a liquor license. The steps of the process for licensing your business include:
1. Managing the Key Requirements of Operating Your Business
You have to choose a business structure for your business - either a sole proprietorship, a partnership or a corporation. You probably need an attorney to advise you on the types of corporations and to register the corporation, DBA name of the restaurant, etc. If you decide to name your restaurant something catchy other than your legal name, you have to register your restaurant’s Fictitious Business Name to open a bank account under the name and be recognized as a legal entity in court proceedings.
EIN or Employer's Identification Number
You must register with the federal government and get an EIN for your food business. The EIN identifies your company to the IRS and allows you to withhold funds from the payroll of your employees for federal taxes. You will also use the number for making your estimated tax payments on business profit. Registering is free, and you can get your number online at irs.gov.
Fictitious Business Name
In Texas, DBA names, also called Fictitious Business Names, are registered in the county where your business operates. Houston is in Harris County, so you must register your restaurant and the name under which you plan to do business at the Harris County Clerk Office.p>
You must first search the Clerk’s database to see if the name you’ve chosen is available. If it is, the cost is $15. If you are operating a food truck, you might encroach into other counties, and it’s necessary to get licensed in any county where you operate.
2. Registering for Your Business License
There’s actually no general requirement for a business license in Houston, but restaurants need a Retail Food Establishment Permit. The cost of the permit is based on your estimated gross sales, and the fee will be adjusted if your estimate is short or overly optimistic. The annual fee runs between $258 and $773. You can get further information at houstontx.gov.
Texas Sales and Use Tax
You must register with the state to get your number to collect Texas Sales and Use Tax. Registering with the state gets you a number and authorization to collect sales taxes on your restaurant sales. Raw food items used in your restaurant aren’t subject to sales tax, so you don’t need to issue a tax exemption certificate for most food items you buy for resale.
The state imposes a 6.25% sales tax on almost all restaurant food sales - even carryout items not intended for immediate consumption - except for certain bakery items like birthday cakes. As a retail business, restaurants, bars and food trucks collect sales tax on each food sales transaction. This money must be held in trust for the state until you forward it to the Office of the State Comptroller.
Some states tax supplies, but Texas doesn’t charge sales tax on paper goods and carryout materials that are used as integral parts of the meal, such as plasticware, napkins, straws and bags. You can furnish your state number to get an exemption from state taxes on these items if your supplier inadvertently charges tax on these items. Certain kinds of equipment used to process food for resale are also exempt from sales taxes, such as deep fryers, juicers, coffee-related machines, bread machines and many other kinds of equipment.
You can just issue an exemption certificate when you buy items that would otherwise be taxed. Alternatively, you can deduct sales taxes that you paid on exempt products for resale on your sales tax transmittal.
The State of Texas doesn’t have any income tax, so you don’t have to worry about withholding state tax from employee payroll. You also avoid the bureaucratic hassle and expense of filing estimated state income taxes for your business.
3. Getting a Health Department Permit in Houston
Getting a health permit for your restaurant, bar or food truck can be relatively painless in some cases. At other times, you might face a few barriers that take time to manage. If you aren’t making any major changes to a building - such as buying an existing restaurant - getting approved by the Texas Department of State Health Services can be simple. If you’re making structural changes to a building to accommodate your restaurant, things are a bit more complicated.
There are three types of health permits in Texas for food businesses. These include:
- Fixed establishment permits for restaurants, bars, retail food sales, etc.
- Mobile unit permits for food cart vendors, mobile food trucks, and street vendors
- Temporary establishments for popup restaurants and vendors at fairs, festivals, concerts, etc.
The cost of a fixed establishment health permit in Texas, according to dshs.texas.gov, is based on gross annual sales. As of the time this article was written, the cost of a restaurant earning $0 to $49,999 from food sales Is $258. If you earn $50,000 up to $149,999.99, the cost is $515. If you earn more than $150,000 annually from food sales, the permit costs $773. Realistically speaking, most restaurants generate sales higher than $150,000 annually.
Your restaurant must also pass a food safety inspection before your permit is issued. Each employee who handles food must be certified in food safety by passing a course with a 70% or better score from an accredited training program. The cost of the course, exam and Food Handler Card is only $7, and employees can take the course and exam online.
Food Truck Health Permit
You should review the requirements for a food truck permit - if you want to qualify for a mobile health permit. You must qualify for a Food Handler Card, pass a health inspection of your truck and register for Sales and Use Tax collection. The mobile health permit fee is $258 for each unit or vehicle.
Building Codes and Public Safety
Health departments oversee many areas that affect public health and generate safety risks. The DSHS not only inspects and monitors food safety but also inspects business and mobile locations for structural safety and compliance with Houston’s building code. If you must remodel a building for your restaurant, you’ll have to get the plans and construction approved.
According to , you must submit plans for constructing or remodeling a building for restaurant use if the previous tenant was not a restaurant. If you take over an existing food business, plans must be submitted if the remodeling will change the scope of operations, such as changing a sandwich place to a full-service restaurant.
You need to submit plans that include a floor plan, equipment and plumbing elevation details, room finishing materials, equipment to be used in construction and plans for demolition of old structures. The costs of approval and the inspection of finished work vary tremendously, based on the scope of the work, so you should consult the Texas DSHS and the Public Works & Engineering Department for further information
4. Getting a Liquor License
The great State of Texas is widely known as a place that respects the basic rights of people to conduct their own affairs, and that attitude is reflected in its simpler Alcohol Beverage Control regulations. In some states, you might not get a liquor license if you have a blemish on your record back in your school days. According to the Texas Alcoholic Beverage Commission, it only takes 45 to 60 days to get a liquor license. That’s quite a difference from getting a liquor license in California, where it takes tremendous time, money and bureaucratic red tape.
The requirements for restaurant and bar owners to get approved by TABC include the following:
- No felony convictions within the past 5 years
- No moral turpitude violations within the last 6 months
- No violations of state liquor laws within the past 2 years
The application process includes submitting an application to the TABC, getting a Certificate of Occupancy from the Public Works & Engineering Department, getting all city, state and federal licenses and registration and submitting a prequalification to the ARA for location approval.
The costs of getting a liquor license in Texas can range from $12,000 up to $400,000, but the rate for most small restaurants and bars is affordable. You can get a beer and wine license for just $3,000. When getting your license, you should also plan for the costs of buying inventory, which can be quite high for a full bar.
Nurturing Environment for Nurturers
Restaurateurs wear many hats: therapist, manager, cook, first aid provider, accountant, social assistant and others. Essentially, restaurant owners nurture their customers with good food, beverages and empathetic support. Opening a Houston restaurant is easier than doing so in most other cities because the city has a nurturing pro-business attitude and love of all kinds of cuisine. You can operate successfully in an urban area with a big profit potential while enjoying a friendly, neighborhood-type system of support - as long as you pay it forward by nurturing your customers with great restaurant experiences.